Table of contents
No headings in the article.
This episode deals with the layers of networking (OSI model)
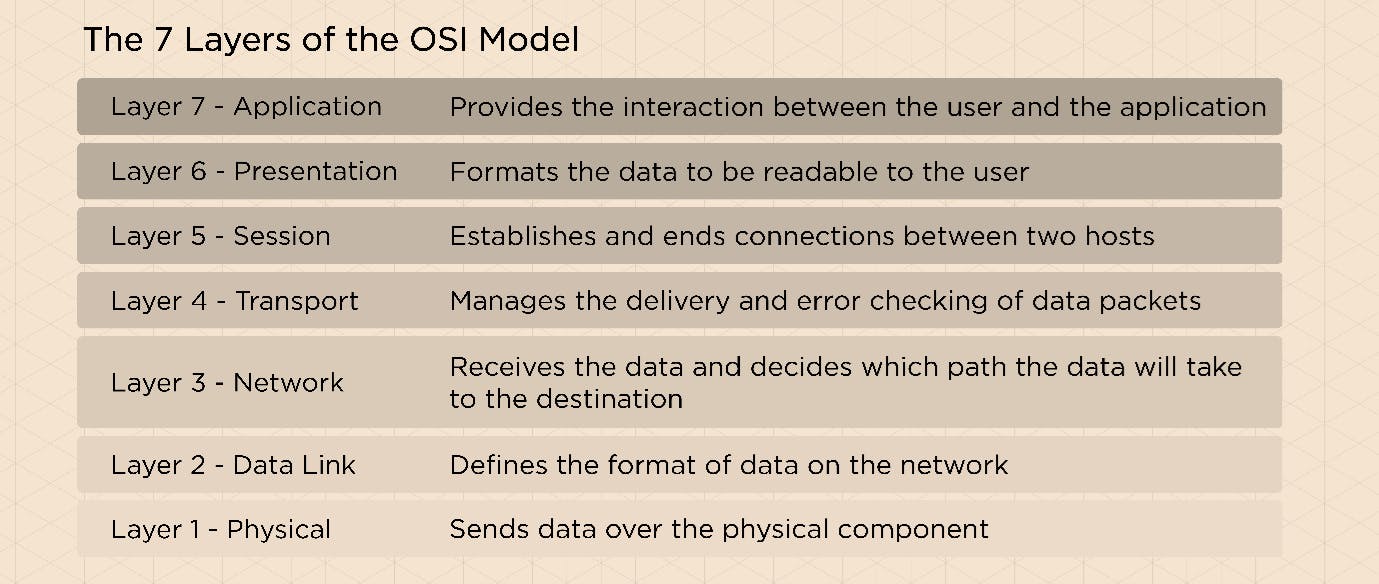
If Devices need to communicate network is required and all the devices have to speak the same language, the communication framework used for this purpose is called the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection). This is also known as the 7 layer model . This model describes how information transfers between the various networking components. This 7 layer model is a theoretical model and in practice only 5 layers are being used to communicate.
Layer 1
Physical layer is the bottom most layer which represents the physical and electrical components including cables, RF links, servers switches etc The first step in troubleshooting the network issue is to check if the physical components are properly connected- like the power plug in place, LAN cable connected to the router etc.
Layer 2
Data link layer as the name suggests is responsible for linking the devices. This layers corrects errors if any at the physical layer and also defines the protocol. This layer breaks the packets into frames and transmits them. Data Link layer is further divided into two sub-layers
Media Access Control Layer (MAC) controls the way a network gains access to media and allows the transmission of data.
Logical Link Control Layeris responsible to identify and encapsulate network protocol and helps in finding errors.
Layer 3
Network layer is responsible for couple of things. First is to break the data into packets (Which is the lowest unit of data transferred over the network. Packets are like the envelopes which carry the data from one device to the other. Second function of this layer is to routing the packets by selecting the best and the shortest path.
Layer 4
Transport Layer is the courier personnel who ensures the message is delivered to the destination reliably. This layer has the following functions
o Controls Flow to ensure the device that transmits does not send more data than that can be handled by the receiving device. o Sequencing packets for segmenting and remote reassembly. o Handling Error and acknowledgments so the data is retransmitted if required. o Combining data from several sources by Multiplexing and transmitting over one data path. o Establishing session between devices with Virtual circuits.
Layer 5
Session Layer is where two devices speak to each other by creating a session. Functions of this layer include setting up, co-ordination and termination among the applications at the session ends. Network Basic Input output system(NetBIOS) does most of the work by providing services relating to the session layer and allows applications on different computers to communicate over a local area network.
Layer 6
Presentation Layer is the layer which prepares the data for the next layer by defining how devices should encode, encrypt and compress data enabling it to be received correctly on the other end. The presentation layer prepares the data for transmission over the session layer.
Layer 7
Application Layer is the closest layer to the user and allows to interact with the data using a specific application or software.
In the forthcoming episodes we would deal with each layers and their standards.
Community and Social Footprints : Sunitha Shenoy : linkedin.com/in/sunithashenoy GitHub github.com/cloudnloud Twitter twitter.com/cloudnloud YouTube Cloud DevOps Free Trainings : youtube.com/c/CloudnLoud Linkedin Page : linkedin.com/company/cloudnloud Linkedin Group : linkedin.com/groups/9124202 Discord Channel : discord.com/invite/vbjRQGVhuF Dev : dev.to/cloudnloud
Subscribe to our newsletter Read articles from Cloudnloud Tech Community directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.

