Public Key Infrastructure
What is PKI?
Set of processes/rules/procedures/policies which create/manage/store/revoke the digital signature and manage public key encryption.
It uses two sets of keys - Public key - shared with anyone you connect and Private Key -shared only to a known person
It is the most common method of encrypting the data between web server and browsers
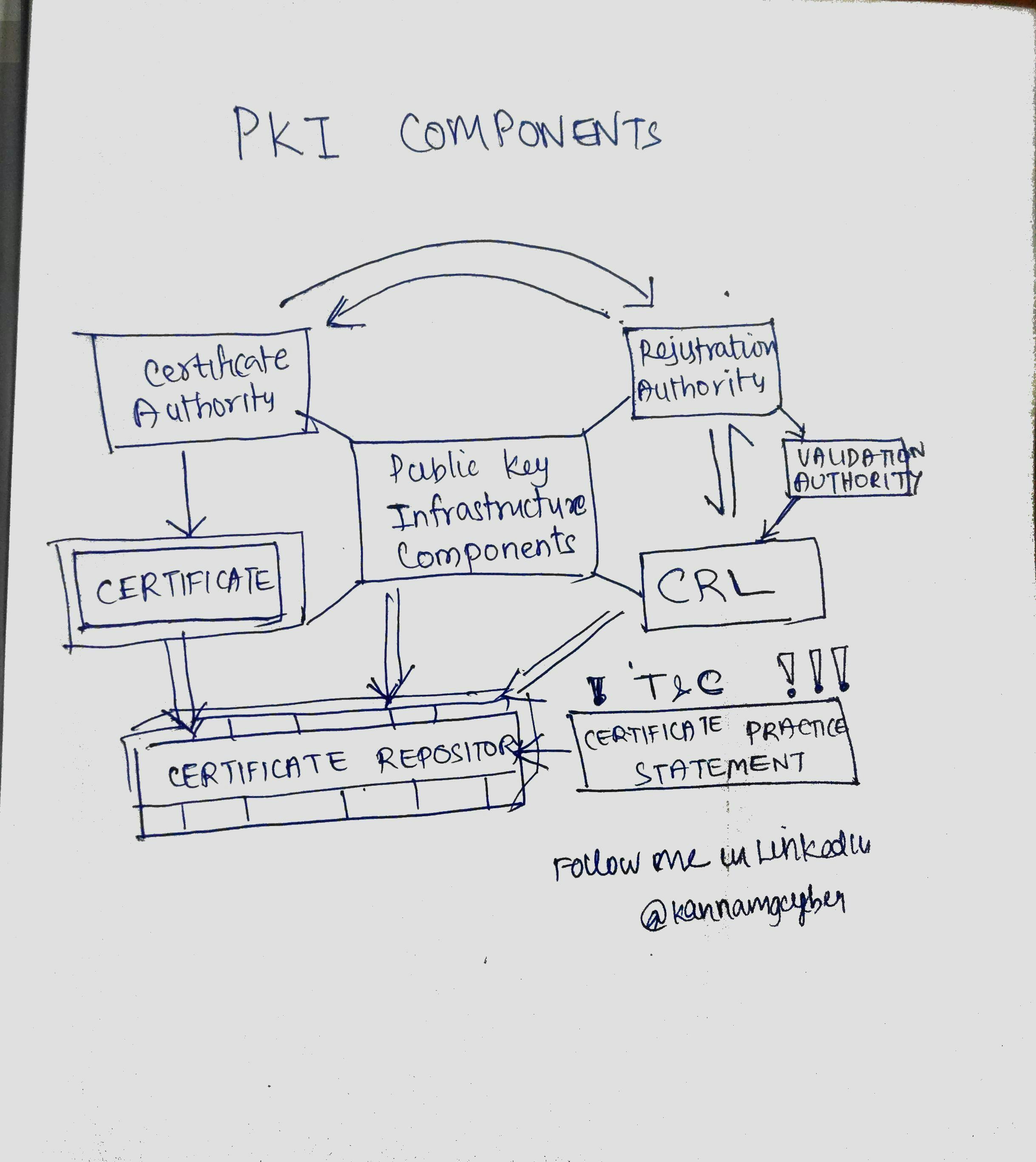
Components of PKI
Certificate: A digital document, signed by a CA, and used to prove the owner of a public key, within a PKI. The certificate has several attributes, such as usage of the key, Client authentication, Server authentication or Digital signature and the public key. The certificate also contains the subject name which is information identifying the owner. This could be, for example, a DNS name or IP address.
Certificate Authority (CA) - is an authority in a network that issues and manages security credentials and public keys for message encryption. a CA checks with a registration authority (RA) to verify information provided by the requestor of a digital certificate. If the RA verifies the requestor's information, the CA can then issue a certificate. CA maintains a directory of digital certificates for the reference of those receiving them. It manages the certificate life cycle, including certificate directory maintenance and certificate revocation list maintenance and publication.
Registration Authority (RA)- A person or organization responsible for the identification and authentication of an applicant for a digital certificate. An RA does not issue or sign certificates. RA verifies information supplied by the subject requesting a certificate. A registration authority (RA) is an entity that is trusted by the certificate authority (CA) to register or vouch for the identity of users to a CA and is a component of PKI.
Certificate Revocation List (CRL): Checks the continued validity of the certificates for which the CA has responsibility. The CRL details Digital Certificates that are no longer valid because they were revoked by the CA.
Certificate Repository: A location where all certificates are stored as well as their public keys, validity details, revocation lists, and root certificates. These locations are accessible through LDAP, FTP or web servers.
Certification Practice Statement (CPS) - is a PKI element that provides detailed descriptions for dealing with a compromised private key.
Validation Authority: A VA allows an entity to check that a certificate has not been revoked. The VA role is often carried out by an online facility hosted by an organization that operates the PKI. A validation authority will often use OCSP or CRL to advertise revoked certificates.
Benefits
Confidentiality (only authorized person can read an encrypted message) - Authenticity (Senders sign/encrypt the message so it ensures the recipient that message is not altered during transit) - Non-repudiation (senders can't deny the message/contents sent)

