Deployments before Kubernetes
Before starting what is Kubernetes and lets understand how deployments were taking place before Kubernetes.
we were having three kinds of deployments :
- Traditional deployments.
- Virtualized Deployments.
- Container Deployments.
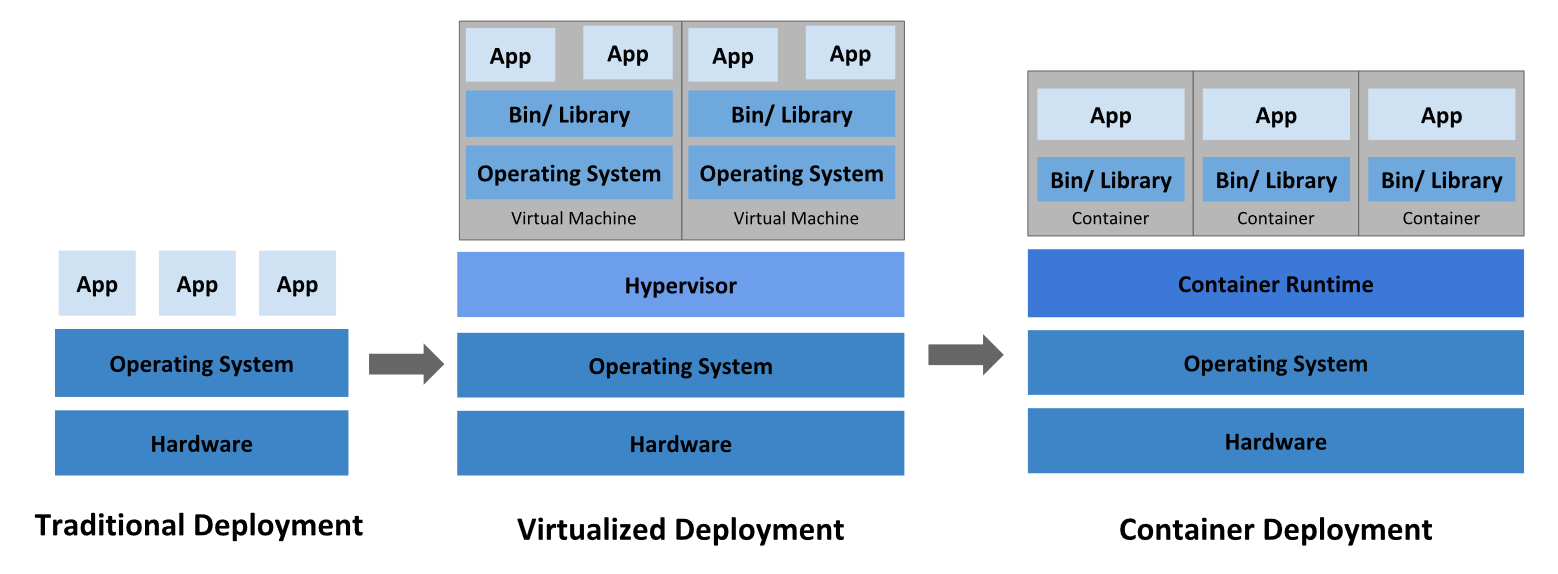
In the Traditional deployments we have our server/machine on which we were installing our OS and on that OS we are running our application. But what if you want to expand your business and also user base is also increasing which requires your application to be upgraded what we will you do ? you will install more servers which will cost you more, their maintenance, resource consumption will also increase etc. Then we moved to another kind of deployments which is Virtualized Deployments.
In Virtualized Deployments we have the same setup with that we have one hypervisor on which we can run multiple OS and on top of that we can run our application and also if we want to scale up we can install multiple OS but we have limitation with that also as those guest OS will consume your machine resources which will be slow at some point and cant serve high requests. Then we move to another kind of deployments which is container deployments.
In Container Deployments we have same setup with container runtime engine on which OS will be running in the form libraries and on top of that OS we are running our application with containerization its become easy deploy our application as it spins up faster and as well as requires less resources.
Why We Need Kubernetes ?
In docker we maintain containers on the machines but what if machines gets crashed then we are no able to access that container. Here is the role of Kubernetes. Kubernetes forms a cluster in which it has several machines connected and on top of that cluster the containers are used. The advantage of this is if any machines goes down there will be other machines which serve container.
What is Kubernetes ?
In general Kubernetes is a open source platform and container orchestration tool for automating deployment, scaling and operations of application containers. it follows the concept of Master and worker nodes cluster which are highly available without any downtime or we can say very minimum amount of downtime.
Architecture of Kubernetes.
As we all know There is Master node and Worker node but how this cluster works. There are several components lets see one by one :
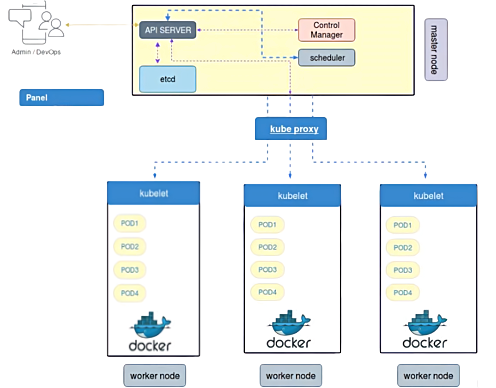
Kubernetes Components
1. API Server
It is use to communicate with other components of different or within server. If server wants to communicate with other components it will be done via API server these should be exposed to HTTP. Instead of communicating through port e can easily communicate via API.
2. ETCD
ETCD stores the configuration information which can be used by each node in the cluster. ETCD is Consistent and highly-available and store the data into key value format used as Kubernetes' backing store for all cluster data and It stores all the data used to manage the cluster. It is accessible only by Kubernetes API server.
3. Controller Manager
Controller Manager is responsible for all the activities in the cluster whatever changes that has to be done that will be approved by controller manager. Before doing any changes it will check the old configuration in the ETCD then it will approve the changes and will commit those changes in the ETCD as well and id the changes are not executed properly then it will not commit those in the ETCD.
There are Different Controller in the control pane each one has separate Process. They are all compiled in a single binary and working in a single process Some types of controller are :
- Node Controller : It is mainly responsible for noticing and responding when any of the nodes goes down.
- Job Controller : It is responsible for creating pods to run the tasks so that it can be completed. it keep on watches for the job and creates the pod for the same.
- Endpoint Controller : It is responsible for provisioning the endpoints such as service endpoints,pods etc.
- Service Account & Token controllers : It is responsible for creating defaults services account, API token access for namespaces.
4. Scheduler
It is responsible for carrying out the instruction specified by controller manager. It is responsible for triggering the changes on particular cluster. It also responsible for tracking the utilization of the workload on cluster nodes. and then placing the workload on which resources are available and accepting the workload.
5. Kubelet
It act as a agent it will receive the request and whatever the changes the control manager has assigned kubelet agent will make sure it should be applied correctly and give success or failure feedback. If Kubelet is not working the cluster will not be able to control the workload.
6. Kube Proxy
It is a network proxy which run on each node in the cluster. It maintains the network rules on nodes these rules allow network communication on your pods from network session inside or outside of the cluster.

