What is IT Infrastructure
IT infrastructure is a group of IT components—hardware, software, networks and resources—that work together to help develop, test, deliver, monitor, control and sustain an organization's IT environment. A well-managed IT infrastructure ensures business continuity in an organization and better connectivity, productivity and security. The computer infrastructure should be regularly updated in accordance with technological progress. Updated infrastructure is reliable, secure and helps achieve business objectives, providing a competitive advantage in the marketplace. The right IT infrastructure also protects against cyber attacks, downtimes and other events that interfere with the proper conduct of business. The foundational components of any IT infrastructure are.
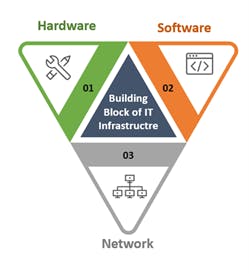 Hardware :
Hardware refers to all the parts, components, and equipment that are used to maintain an organization's IT infrastructure.
Hardware :
Hardware refers to all the parts, components, and equipment that are used to maintain an organization's IT infrastructure.
Software :
The software is an infrastructure component that needs extra hardware as a host environment. Hardware and software collaborate to form a global IT set-up.
Network :
Networks include hardware and software components as well as configurations that you configure to control and manage network access for a variety of users.
Infrastructure Architecture types
An IT infrastructure architecture defines the way you design and structure your IT components for better performance, simplified management, scalability and cost-effectiveness. You can choose from a number of different types of IT infrastructure architectures, depending on your organization's size and nature. The following are the different types of IT infrastructure architectures
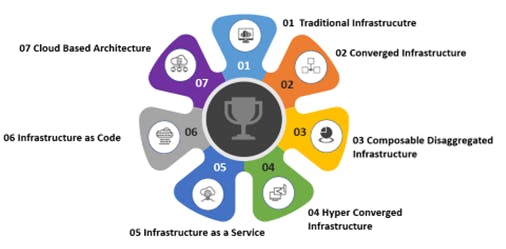
1. Traditional infrastructure
In a traditional architectural design, IT components generally exist onsite and in silos.The company purchases the majority of IT equipment and software and relies primarily on an internal team to operate the engines.Different sites can be managed by different IT teams and business unit, office and regional systems are siloed.This type of IT infrastructure architecture can be found in small to mid-sized, non-digital Indigenous organizations.
2. Converged architecture
This kind of IT infrastructure architecture aims to overcome the fragmentation of traditional infrastructure. It consolidates the associated IT components into one optimised hub and implements connected workflows for centralized visibility.Available resources are grouped into "resource pools" shared through different applications and processes according to priorities and operational policies.Cloud computing has also allowed for the convergence of IT infrastructure architectures, making it easier to consolidate, centralize and disburse resources.
3. Composable disaggregated infrastructure
This is a convergent architecture subtype but uses computer components on site. This emerging technology enables physical data centres to act as a virtual host so that resources can be allocated upon request.The disaggregated composable infrastructure is powered by high-speed, low-latency networks that enable quick resource allocation and minimum downtimes. Such IT infrastructure architecture is an emerging alternative for major digital companies.
4. Hyper-converged infrastructure
Hyper-converged infrastructure uses software components hosted on a hypervisor to achieve this, breaking down silos and enabling centralised management, similar to a converged IT infrastructure architecture. Its essential elements consist of software-defined networking, storage, and, of course, the hypervisor, which enables resource federation between processes.Commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) servers are typically used to run this type of IT infrastructure design.
5. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
According to the trend of shifting away from hardware-heavy IT infrastructure architectures, IaaS is anticipated to surpass $202 billion by 2027.IaaS runs on either a public cloud or private hypervisors/virtual machines and substitutes online services for real computing resources and components. Similar to hyper-converged infrastructures, but with a subscription-based licencing model where all IT services are provided and maintained by a third party.
6. Infrastructure as code
It is a specific approach to IT infrastructure management that allows the architecture to be maintained and manipulated using software applications or lines of code rather than physical hardware configurations or configuration parameters. UI. Infrastructure is applied as code to computer components of hardware and software, with strategically applied code that helps control operations, provide resources, enforce security, and perform other activities.
7. Cloud-based architecture
The cloud is rapidly becoming the standard environment for hosting computer infrastructure components, with the ability to fully migrate to the public cloud, distribute operations between on-premises and cloud environments, have your own cloud, or deploy managed cloud services . Today, most organizations choose the hybrid cloud path, where local and cloud resources are mixed, with private cloud and multiple cloud service providers coexisting.
