What is Kubernetes Deployments?
After reading this post you will be understanding the high level of Kubernetes Deployments, its advantages of this, and basic kubectl commands related to Deployments
If you have not yet checked the previous parts of this series, please go ahead and check this 👉Link
In Kubernetes, Deployment is used to provide declarative updates to Pods as well as ReplicaSets. Also, a Deployment Controller is the higher version of a Replication Controller, as it Removes, Adds, and Updates Pods in ReplicaSets. We need this to work faster and dynamically when we have ReplicaSets with tens of pods, and we are in need to modify them. By using Kubernetes Deployment, this can be achieved with very little effort if used in a correct way.
Deployment sits top of the Kubernetes hierarchy layer. First Pod, then Replica Set, and then Deployment. By using Deployment we can easily upgrade the Pod instances using rolling update and we can easily undo the changes. So Deployment in the Kubernetes cluster is very flexible and gives us more value
Advantages of Deployment in Kubernetes
- We can easily scale the application by creating multiple instances of a single Pod.
- Upgrade the instances seamlessly. The Deployment uses the rolling update concept. The rolling update will update the instance one after another instead of updating all.
- If the updated instances had some error, then we can easily undo the changes by rolling back to the previous version!
How Deployment Works
- First it will create a Deployment. Just a registry for the Pod definition.
- Then the replica set is created for the Pod definition.
- Then the desired number of Pods are created using the replica set.
Two types of deployment strategy
- Destroy all of them and create a new version
Note: During the upgradation, time application is not available This is not the default deployment strategy
- Do not destroy all of them - this is the default deployment Take down the older version and bring up a newer version one by one
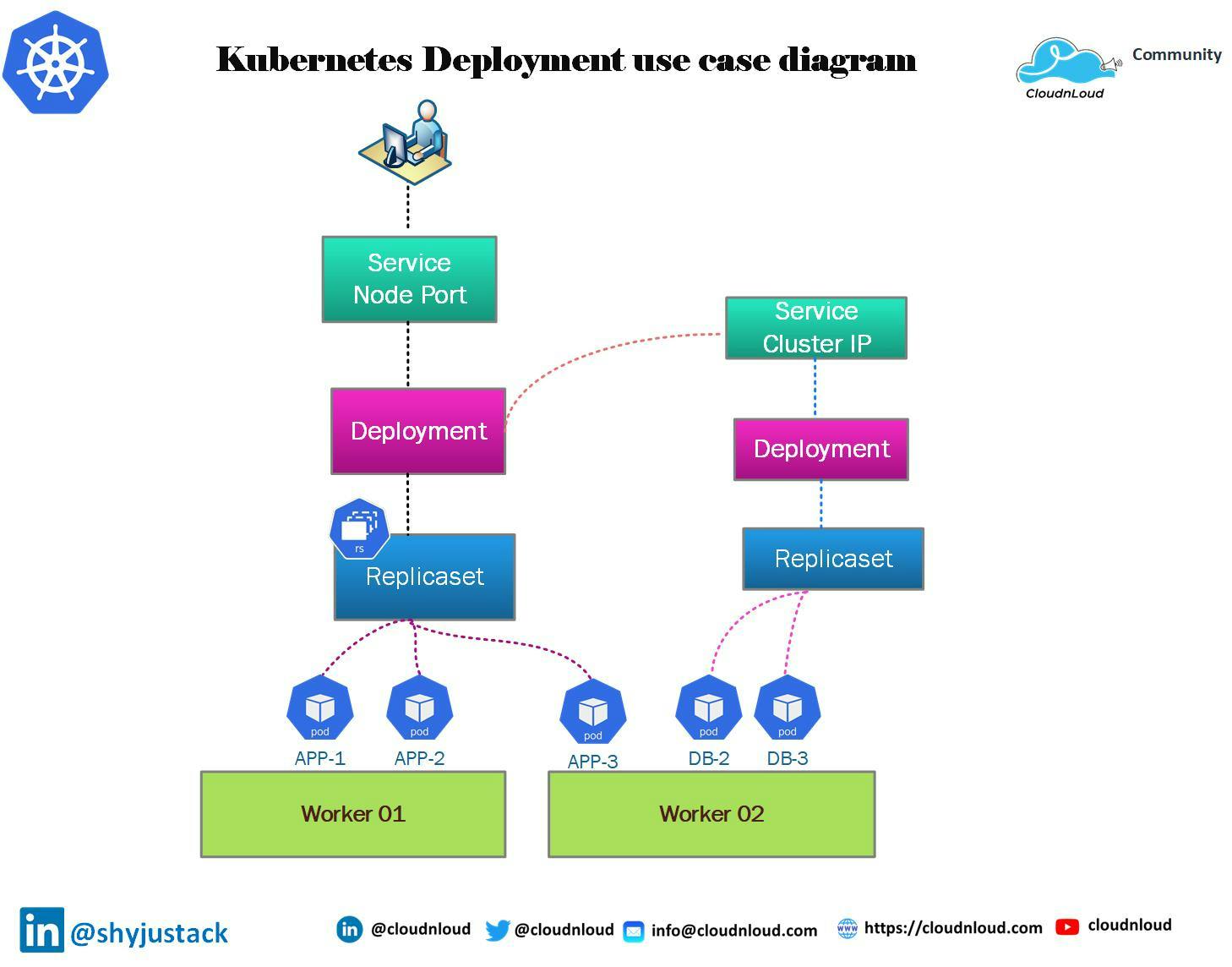
Deployment Use case Diagram
This diagram will help you to understand the application and Database deployment in the Kubernetes cluster
Create Deployment YAML File
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nodeapp-deployment
labels:
app: nodeapp
type: front-end
spec:
template:
metadata:
name: nodejsapp-pod
labels:
app: nodejsapp
type: front-end
spec:
containers:
- name: nodejsapp-erp
image: nginx:1.16.1
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
type: front-end
How to test the deployment status ( you need to check this three status)
kubectl get deploy
kubectl get rs
kubectl get pod
Upgrading the Nginx version
kubectl set image deployment/nodeapp-deployment nodejsapp-erp=nginx:1.19.1
you can upgrade the version through the YAML file, change a particular version value and run kubectl apply -f
Rollout the version
kubectl rollout undo deployment/test-deploy --to-revision=2
Rollout history showing command
kubectl rollout history deployment/test-deploy
How to check the rollout status
kubectl rollout status deployment/test-deploy
Hope you have got an idea about Kubernetes Deployment and how we can implement them in our product environments
Happy Learning 📚
Thank you for reading!!!

