In the previous infrastructure series we discussed the 7 layers of OSI, since beyond this we will be discussing in-depth networking concepts, we would continue as networking series. We shall begin with IP and TCP/IP in this episode Networks use protocol to communicate or perform functions irrespective of the hardware which is underlying.
IP addressing is an important in Network. IP address also known as Internet Protocol Address is numerical label which is assigned to each device in any computer network. IP address keeps changing between network and is crucial for directing messages across networks. IP addresses are made up of four octets example 198.162.1.0, each octet has number between 1 to 255, meaning there could be 254 IP addresses for each octet. Each IP address has 2 parts - a network part and the host part. Network part directs routers to group of devices where the packet should go. Host part directs routers to specific device in that group that the packet should go. Each group of devices on any IP internet should have a singular network part, and every device within that specific group requires an unique host part. For the web,the Network Information Center (NIC) generates all network part assignments by possible unique addresses. The NIC assigns own block of addresses to the internet service providers (ISPs), which is then assigned to their customers.
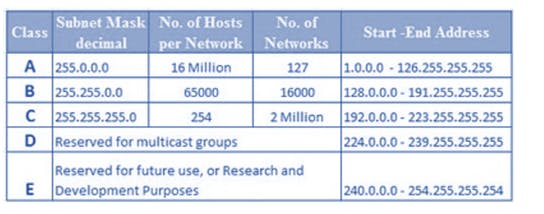
IP address classes
The parts of any provided address comprises the network part and the host part which are determined by the "class" of the network. In all cases, the part of the address which is not used for the network part is left as the host part.
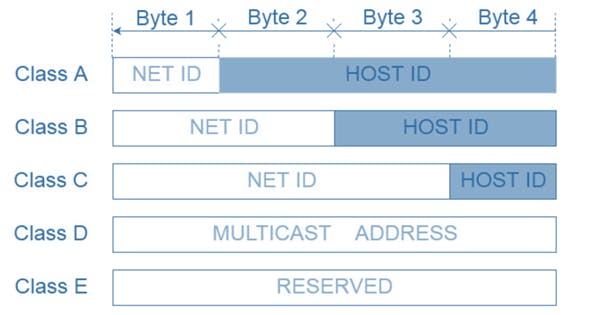
The below break up is no longer used and is replaced by CDIR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing)but would help us understand the sizes of network.
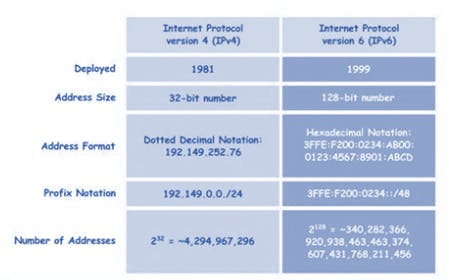
 The IP versions helps to identify devices in a network and there are two main versions of it, IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 addresses ran out in 90s because of the growth and hence was replaced with IPv6 which has an extensive scope of IP addresses.
Here is IPv4 vs IPv6
The IP versions helps to identify devices in a network and there are two main versions of it, IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 addresses ran out in 90s because of the growth and hence was replaced with IPv6 which has an extensive scope of IP addresses.
Here is IPv4 vs IPv6
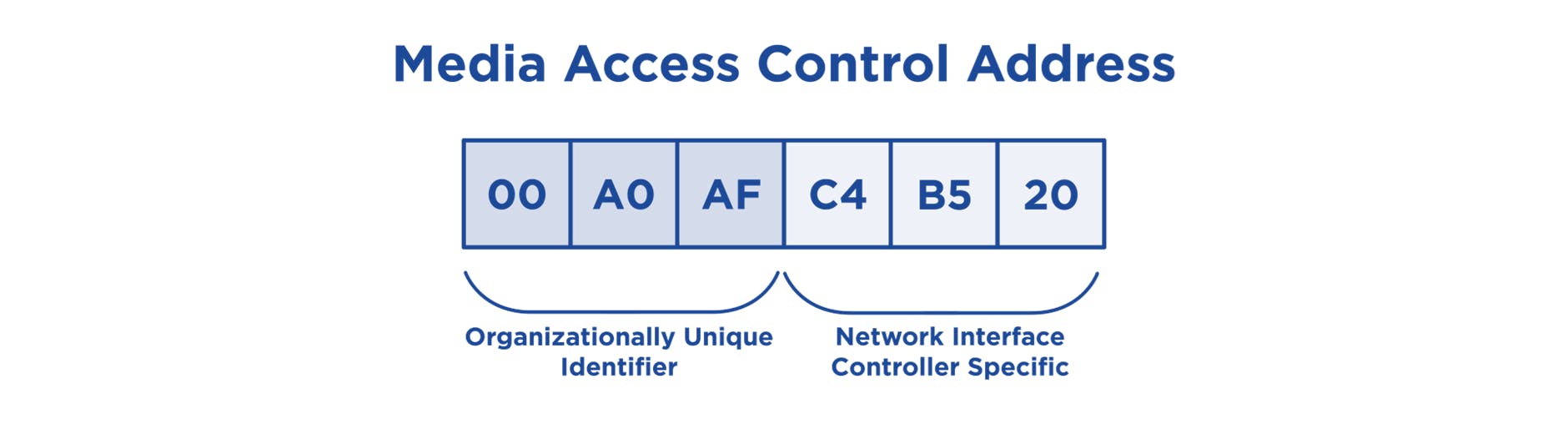
MAC Address Each component of the network has Media Access Control and IP address. As mentioned before IP addresses change if they connect to a different network, but MAC addresses is a physical address which remains constant as it is a unique identifier assigned by the manufacturer. It contains 12 digits represented by 0-9 or A-F Example as below :
 Domain names
We as users use the domain name to access a web instead of IP addresses. Domain names are the name of the site which we type in the address bar e.g google.com.
If we keenly observe the web address it is made of three main parts
Top-level domain - which provides information like the geographical area eg. websites ending with .in are from India, .de from Germany, .fr from France, other examples being .com, .net, .org, .gov- these are owned by Organizations.
Domain name - is the name registered by the organization eg. Yahoo.com, youtube.com etc
Subdomain enables websites to segregate and organize content, eg. blog.hashnode.com blog.dev.com etc.
Domain names
We as users use the domain name to access a web instead of IP addresses. Domain names are the name of the site which we type in the address bar e.g google.com.
If we keenly observe the web address it is made of three main parts
Top-level domain - which provides information like the geographical area eg. websites ending with .in are from India, .de from Germany, .fr from France, other examples being .com, .net, .org, .gov- these are owned by Organizations.
Domain name - is the name registered by the organization eg. Yahoo.com, youtube.com etc
Subdomain enables websites to segregate and organize content, eg. blog.hashnode.com blog.dev.com etc.
Community and Social Footprints :
- Sunitha Shenoy
- GitHub
- YouTube Cloud DevOps Free Trainings
- Linkedin Page
- Linkedin Group
- Discord Channel
- Dev
Subscribe to our newsletter Read articles from Cloudnloud Tech Community directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.

